

Electro-conductive polymer used in solid capacitors helps to achieve the following excellent characteristics:
The Lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) means Less power - solid capacitors are able to deliver substantially lower impedance at higher frequencies. Because there is less impedance, solid capacitors are more stable and generate less heat than electrolytic capacitors. |
Higher Ripple Current absorbs higher power switching that plays a decisive role in motherboard power phase design. Solid capacitors have better capacity for power switching and thus contribute significantly to better motherboard stability compared to electrolytic capacitors. |

Longer Life- More Durable Motherboards
In terms of lifespan, solid capacitors last longer than electrolytic capacitors, especially at lower working temperatures. As the table below shows, at 65°C, the average lifespan for a solid capacitor is more than six times greater than electrolytic capacitors. In actual years, the solid capacitor will last approximately 23 years, while the electrolytic capacitor dies after only three years. Clearly, solid capacitors have a lifetime advantage over electrolytic capacitors.
In terms of lifespan, solid capacitors last longer than electrolytic capacitors, especially at lower working temperatures. As the table below shows, at 65°C, the average lifespan for a solid capacitor is more than six times greater than electrolytic capacitors. In actual years, the solid capacitor will last approximately 23 years, while the electrolytic capacitor dies after only three years. Clearly, solid capacitors have a lifetime advantage over electrolytic capacitors.
Temp°C |
Electrolytic Capacitors (Working Hours) |
Solid Capacitors (Working Hours) |
|
95°C |
4,000 Hrs |
6,324 Hrs |
1.5X longer
|
85°C |
8,000 Hrs |
20,000 Hrs |
2.5X longer
|
75°C |
16,000 Hrs |
63,245 Hrs |
4X longer
|
65°C |
32,000 Hrs |
200,000 Hrs |
6.25X longer
|
High Temperature Capability- More Reliable Motherboard
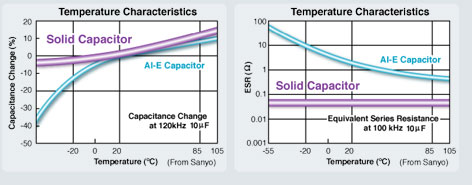
Capacitance of solid capacitors stays stable in sharp changing temperatures - Solid capacitors deliver more stable capacitance and are less likely to be affected by temperature changes. As the chart shows, even at extreme temperatures, solid capacitors have relatively stable capacitance, especially when compared to electrolytic capacitors.
Capacitance of solid capacitors stays stable in sharp changing temperatures - Solid capacitors deliver more stable capacitance and are less likely to be affected by temperature changes. As the chart shows, even at extreme temperatures, solid capacitors have relatively stable capacitance, especially when compared to electrolytic capacitors.
No more Exploding Capacitors - More Stability for over-clocking
Swelling and leaking capacitors have bothered motherboard users for ages. This dramatically lowers a PC's performance, and may even damage the motherboard to the point where it can no longer operate.
As there is no liquid component to solid capacitors they don't leak or explode. In addition, their ability to tolerate extreme conditions and their overall robustness, make them much more suited to extreme operating environments.
Swelling and leaking capacitors have bothered motherboard users for ages. This dramatically lowers a PC's performance, and may even damage the motherboard to the point where it can no longer operate.
As there is no liquid component to solid capacitors they don't leak or explode. In addition, their ability to tolerate extreme conditions and their overall robustness, make them much more suited to extreme operating environments.
Characteristics |
Solid Capacitors |
Electrolytic Capacitors |
| Heat-Resistibility | ||
| Allowable Ripple Current | ||
| ESR in high Frequency | ||
| SMD Production | ||
| Safety | ||
| Environmental Protection |
Summary of Solid Capacitor Features
| • | Solid caps have a low ESR |
| A frequency characteristic of impendence shows an ideal curve Ideal to use as de-coupling capacitor for removing such noise as ripple, spike, digital, static, audio, etc. Able to handle large ripple current Ideal for miniaturization, as a smoothing capacitor of switching power supply. Able to discharge rapidly Ideal for use as back-up capacitor in a circuit where large current is consumed at high-speed. |
|
| • | ESR of Solid is not that affected by temperature |
| The Solid cap can be used for low temperature specification equipment ( 0°C or less) |
|
| • | Solid caps enjoy a longer life |
| You can expect to use Solid caps for 20,000Hrs (3 ysears) at 85°C Ideal for devices that should last for a long period. |