Experience RAIDIX 5.X for GIGABYTE platforms
RAIDIX 5.X software enables you to deploy all-flash and hybrid storage with a high-speed block (SAN) and file (NAS) access. Empowered by innovative RAID technologies, RAIDIX provides stable workflow and outstanding performance for data-intensive tasks.
In cooperation with GIGABYTE, the RAIDIX team have come up with a number of enterprise-scale software solutions that can make a huge difference for a business, both technological and financial.
In cooperation with GIGABYTE, the RAIDIX team have come up with a number of enterprise-scale software solutions that can make a huge difference for a business, both technological and financial.
RAIDIX 5.X + GIGABYTE Solutions
Ultra-high bandwidth for the most demanding tasks
Internal logic of RAIDIX storage arrays was originally developed to get maximum benefits for working with massive sequential workloads.
The lowest impact of hardware failures
RAIDIX has dual controller configuration to eliminate single point of failure and prevent impact from the most common hardware failures.
Easy integration into existing infrastructure
RAIDIX data storage works with any drive from any vendor. Software-driven architecture eliminates storage vendor lock-in.
Ready for non-standard projects
Due to simple integration with parallel file systems, RAIDIX data storage can be easily adjusted to outsized and non-trivial installations.
NearLine Media Solution
NearLine storage is a great configuration for ‘cold-ish’ data, not ready to be archived yet. GIGABYTE-RAIDIX joint solution is ready to keep the data safe, with overall costs such as $50/TB, using fast SAS/SATA SSDs.
Tech Features
• Scalability up to 9 PB
Tech Features
• Scalability up to 9 PB
• Stable high read performance
• Proprietary RAID 7.3, N+M levels
• Wide range of supported interfaces
Business Impact
• Reduces costs and complexity of modern workflows
• Guarantees the availability and preservation of very expensive content with minimal investment in infrastructure
• Reducing the time required to implement centralized storage
• Low storage footprint
Business Impact
• Reduces costs and complexity of modern workflows
• Guarantees the availability and preservation of very expensive content with minimal investment in infrastructure
• Reducing the time required to implement centralized storage
• Low storage footprint
HPC Storage & AI Solution
Enterprise-scale solution improves the cluster efficiency by up to 30%, which leads to an overall saving of 50% of the storage system's TCO. Efficiency is provided by patented RAIDIX algorithms, implemented in RAIDIX 5.X.
Tech Features
Business Impact
• Less time to get insight
• Less time to teach NL
• The minimum entry point
• Fully integrated solution from single hands
Tech Features
• Random IOPS optimization
• Lustre/BeeGFS integration
Business Impact
• Less time to get insight
• Less time to teach NL
• The minimum entry point
• Fully integrated solution from single hands
Enterprise Backup Target
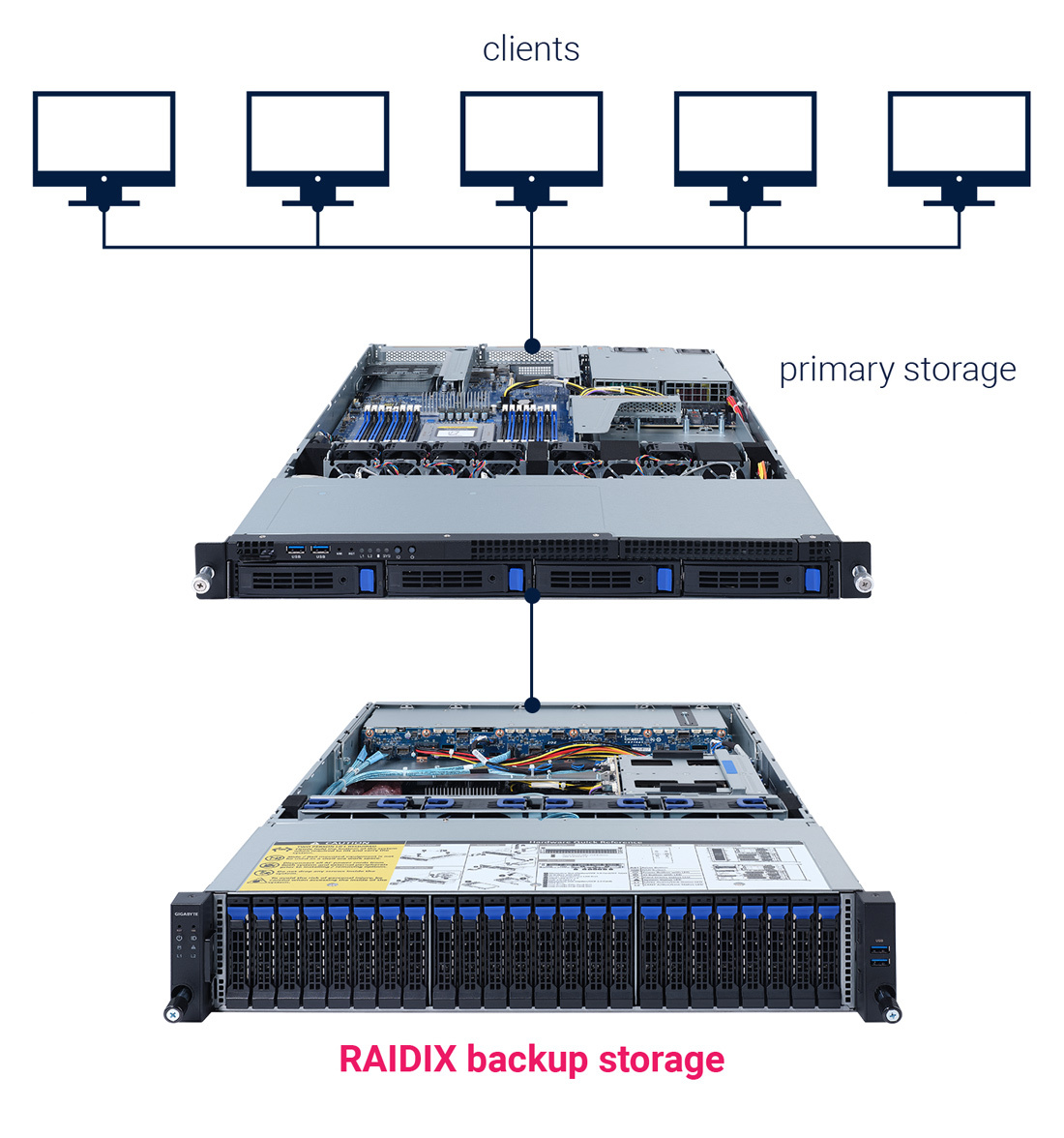
While many see backup storage as something you should not splash out on, this part of a storage system becomes decisive when trouble comes (as it usually does). As a result, cheaper backup hardware often fails to provide full recovery.
GIGABYTE-RAIDIX joint solution has a smart way to go about it, as it checks the backup data regularly, and substitutes it if necessary. As a result, RPO and RTO fall dramatically.
Also, the solution provides a much better performance rate than competitors: as it provides scalability up to 9 PB (4x better), write speed 70TB/hr (average market 50TB/hr), and the proprietary RAID N+M level.
Tech Features
GIGABYTE-RAIDIX joint solution has a smart way to go about it, as it checks the backup data regularly, and substitutes it if necessary. As a result, RPO and RTO fall dramatically.
Also, the solution provides a much better performance rate than competitors: as it provides scalability up to 9 PB (4x better), write speed 70TB/hr (average market 50TB/hr), and the proprietary RAID N+M level.
Tech Features
• Scalability up to 9 PB
• Proprietary RAID 7.3, N+M levels
• High write bandwidth
Business Impact
• Improves RPO/RTO
• Low TCO
• Low storage footprint
Large Video Surveillance Solutions
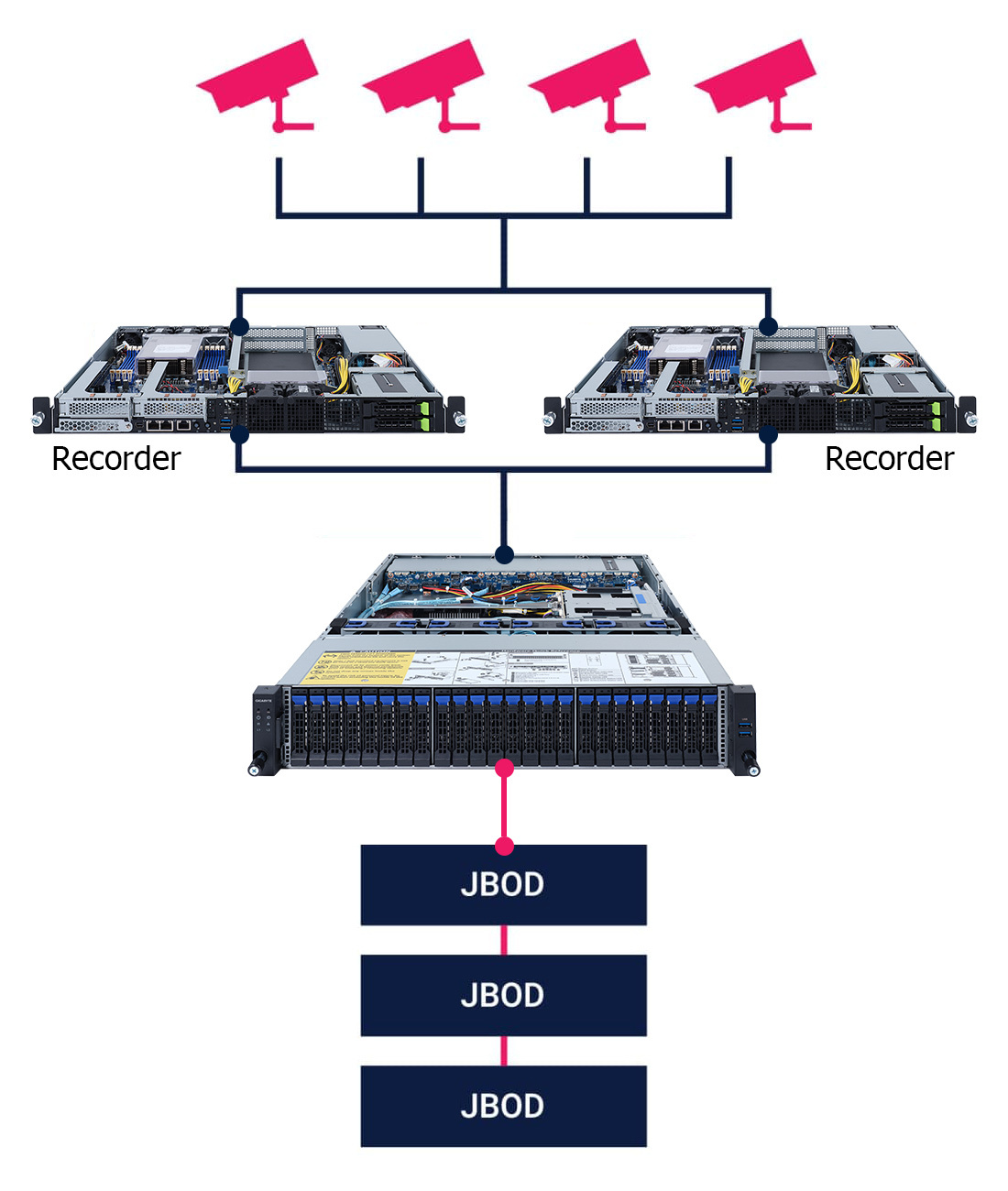
As VSS gets bigger and more complicated, the demand for fast archive access grows. GIGABYTE-RAIDIX delivers undisruptive archive access, which saves time and money necessary for ensuring safety.
Tech Features
• Scalability up to 9 PB
• Proprietary RAID 7.3, N+M levels
• High write bandwidth
Business Impact
• Reliable archive access
• Optimized data workflow leading to less TCO on large projects
Tier 2 Storage Apps
Tier 2 Storage Apps
Tier 2 applications may take up a lot of storage space. Joint GIGABYTE-RAIDIX solution brings cost-effectiveness to those apps with storage costs at just 50$/TB.
Tech Features
• Proprietary RAID 7.3, N+M levels
• High Write Bandwidth
Business Impact
• Low TCO
• Low storage footprint
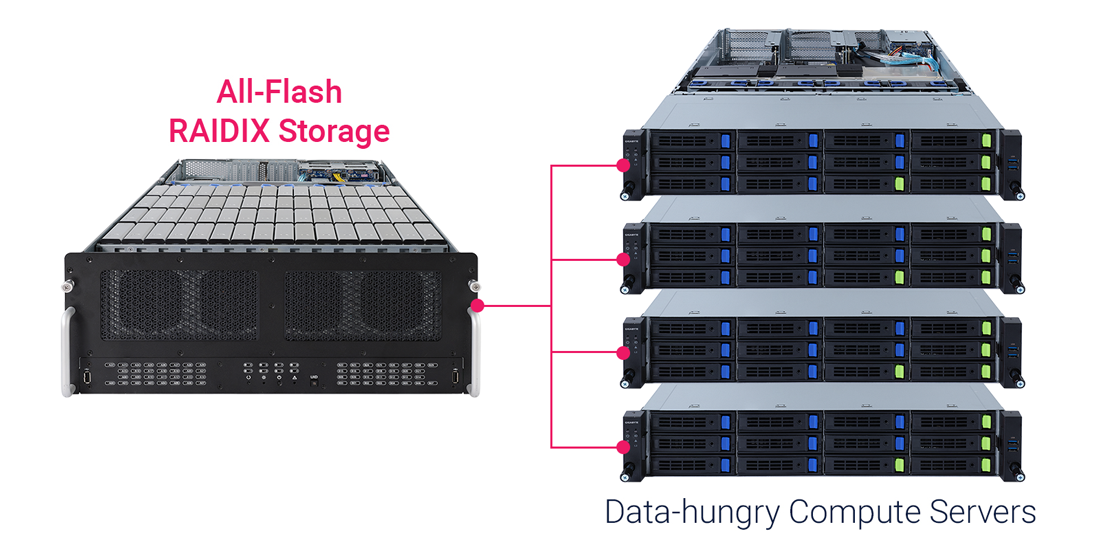
All-flash Media Storage
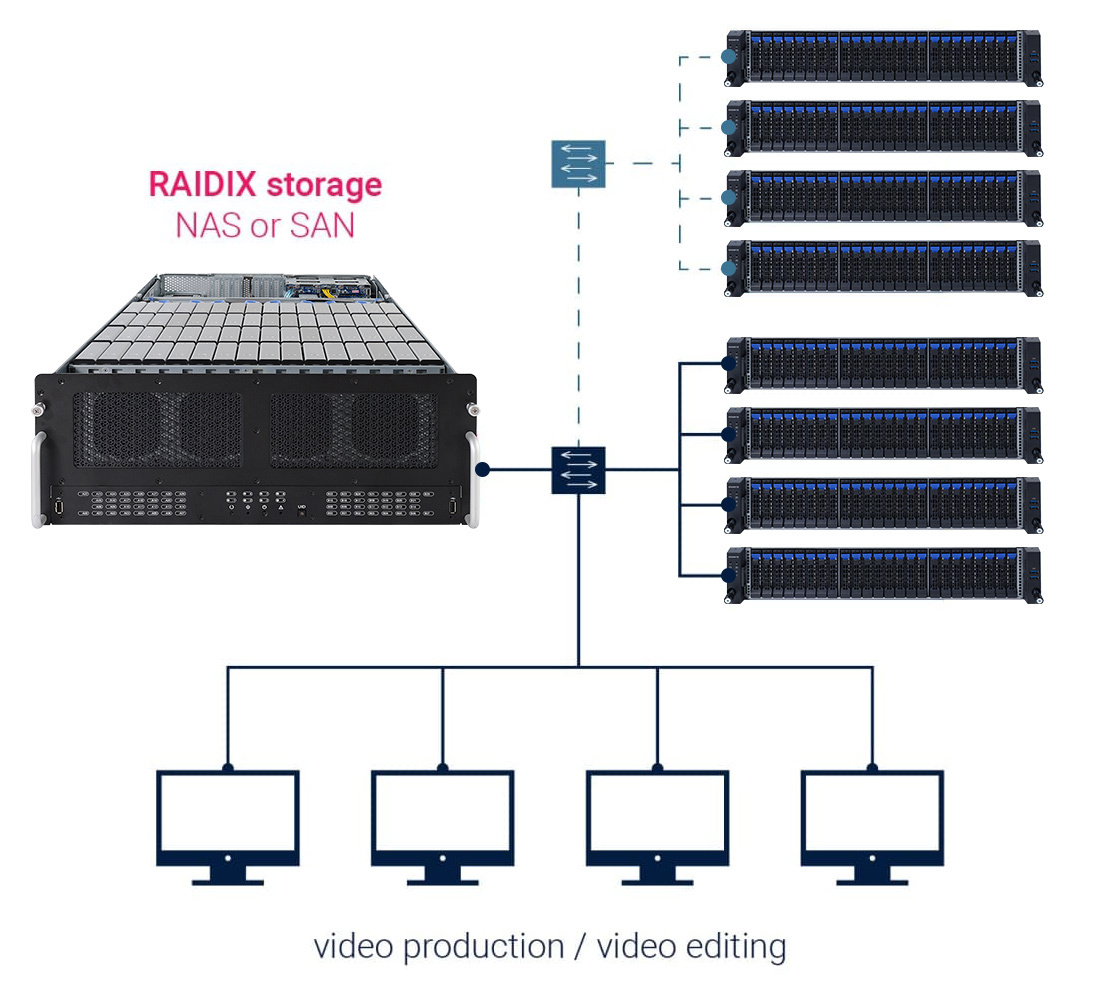
Introduction of new media production technologies leads to better quality — and bigger volumes, and expenses tend to grow similarly. But with All-Flash Media Storage solution by GIGABYTE and RAIDIX you will be ready to work with 16k, with no additional investments needed. Implementation of Hi-End AFA is also possible with the same standard components.
Tech Features
• High Bandwidth (up to 40GBps)
• Random IOPS optimization
Business Impact
• 4k/8k editing and finishing at low cost
• Reducing the time required for rendering, which leads to reduction in costs
What else RAIDIX 5.X has to offer?
Ultra-high bandwidth for the most demanding tasks
Internal logic of RAIDIX storage arrays was originally developed to get maximum benefits for working with massive sequential workloads. It significantly boosts HDDs performance even in low-end storage systems.
To interoperate with solid state drives, RAIDIX storage uses ERA Engine, an innovative software RAID with I/O handling parallelization and lockless data path. These features raise up storage performance to the level of flash potential bandwidth. Moreover, the system shows high IOps and low latency even in mixed I/O workloads like VDI and financial transaction processing.
Internal logic of RAIDIX storage arrays was originally developed to get maximum benefits for working with massive sequential workloads. It significantly boosts HDDs performance even in low-end storage systems.
To interoperate with solid state drives, RAIDIX storage uses ERA Engine, an innovative software RAID with I/O handling parallelization and lockless data path. These features raise up storage performance to the level of flash potential bandwidth. Moreover, the system shows high IOps and low latency even in mixed I/O workloads like VDI and financial transaction processing.
The lowest impact of hardware failures
Driven by innovative RAID technologies, RAIDIX storage demonstrates minimum performance penalty when a drive goes out. It helps to maintain smooth application workflow and data integrity in case of emergency.
RAIDIX has dual controller configuration to eliminate single point of failure and prevent impact from the most common hardware failures.
To protect data from natural and man-driven disasters, RAIDIX can create synchronized copies of data in a secondary data center.
Easy integration into existing infrastructure
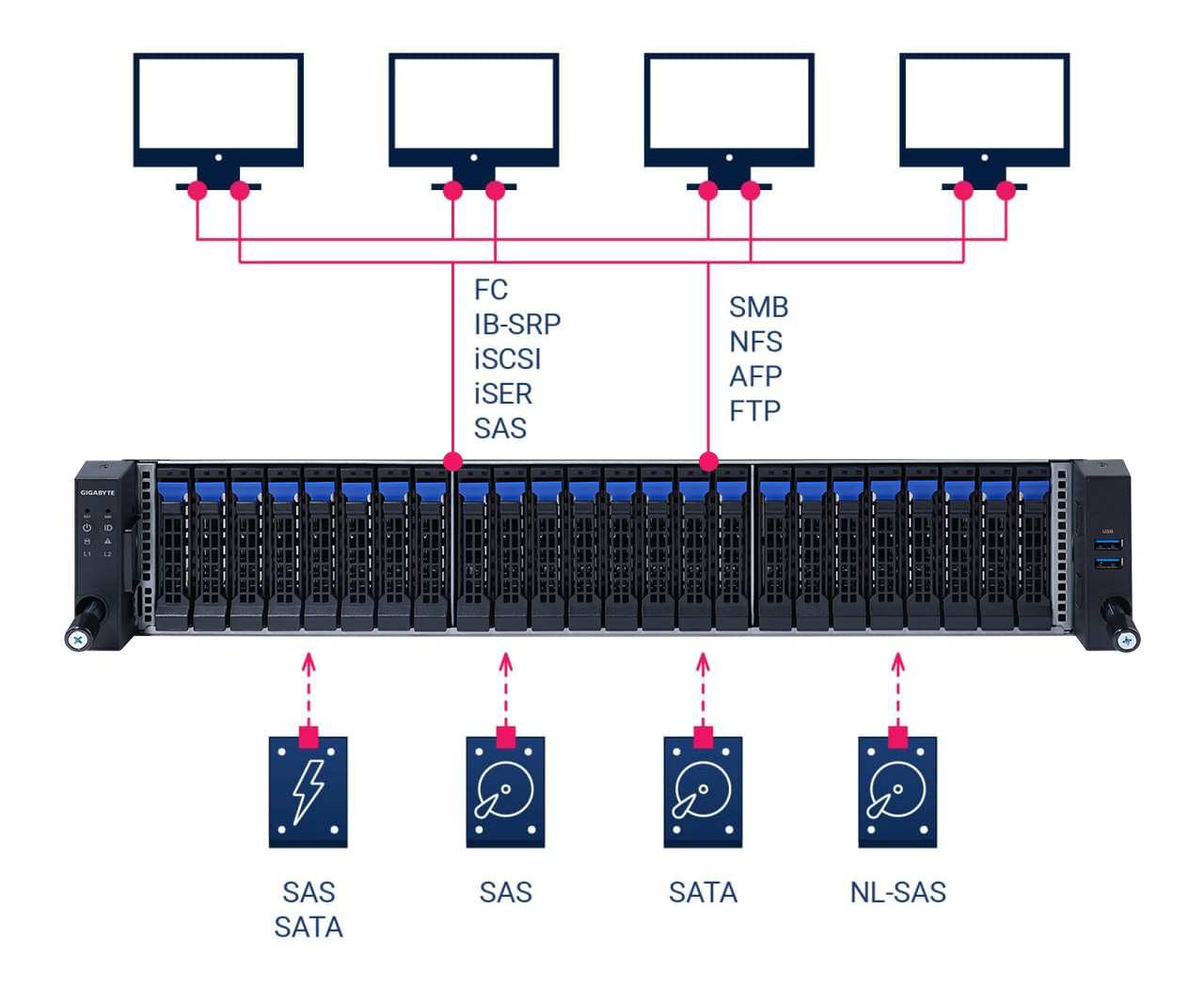
RAIDIX storage provides access via file (NFS, SMB, AFP, FTP) or block (FC, IB, iSCSI, iSER, SAS) protocols*.
To provide more hardware freedom, RAIDIX data storage works with any drive from any vendor. Software-driven architecture eliminates storage vendor lock-in and minimizes costs of regular hardware modernizations.
*file and block protocols cannot be provided at the same time




