Introduction
Two-phase Immersion cooling is a new type of cooling technology for data centers. In a two-phase immersion cooled system, electronic components are submerged into a bath of dielectric heat transfer liquid, which is a much better heat conductor than air, water or oil. With a low boiling point at 50°C, the fluid boils on the surface of heat generating components, and rising vapor passively takes care of heat transfer.
In contrast to submersion oil cooling, two-phase immersion cooling liquids are clean, environmentally friendly and non-flammable. No pumps and jets are required to keep hardware cool. Circulation happens passively by the natural process of evaporation and without spending any extra energy. It is this simplicity that eliminates conventional cooling hardware and results in better cooling efficiency. Compared to traditional air, water or oil cooling, this passive process results in the use of much less energy.
In contrast to submersion oil cooling, two-phase immersion cooling liquids are clean, environmentally friendly and non-flammable. No pumps and jets are required to keep hardware cool. Circulation happens passively by the natural process of evaporation and without spending any extra energy. It is this simplicity that eliminates conventional cooling hardware and results in better cooling efficiency. Compared to traditional air, water or oil cooling, this passive process results in the use of much less energy.
Usage Scenarios
Advantages of Two-Phase Immersion Cooling
Higher Efficiency and Energy Savings
>90% efficiency advantage in the data centers compares to air cooling - including server power consumption and air conditioning costs.
Improved Reliability
Components are not subject to temperature variations, reducing failure potential & no cooling fans required, eliminating degradation from vibration.
Higher Computing Density
No need for heat sinks and cooling fans means computing parts can be placed closer, which can increase computing power by 10 times in the same space.
Lower Maintenance Requirement
Passive cooling system means no unnecessary parts to build or service, useful especially for remote locations such as edge computing stations.
Deployment Flexibility
No air conditioning and low maintenance requirements, it can be shrunk to expandable modules and deployed in confined spaces and extreme environments.
How Does Two-Phase Immersion Cooling Work?
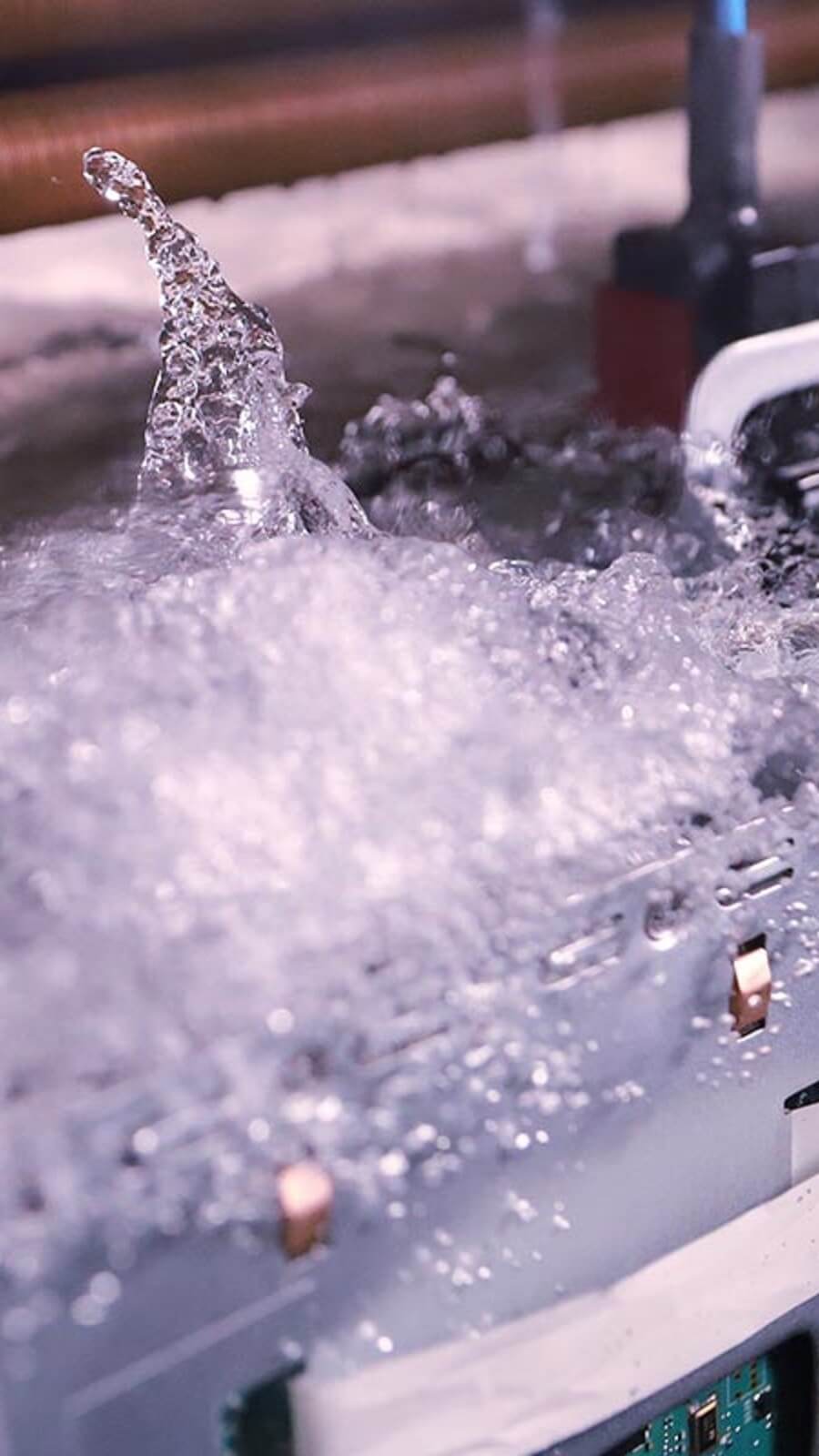
Servers or other IT components are submerged in a thermally conductive dielectric liquid or coolant. Heat is removed from the system by circulating the liquid into direct contact with hot components, whereby the liquid undergoes a low-temperature evaporation process to cool the hot components and transfer the heat out of the liquid. The gas is cooled again by a heat exchanging method such as a condenser coil to allow return flow into the larger liquid volume.
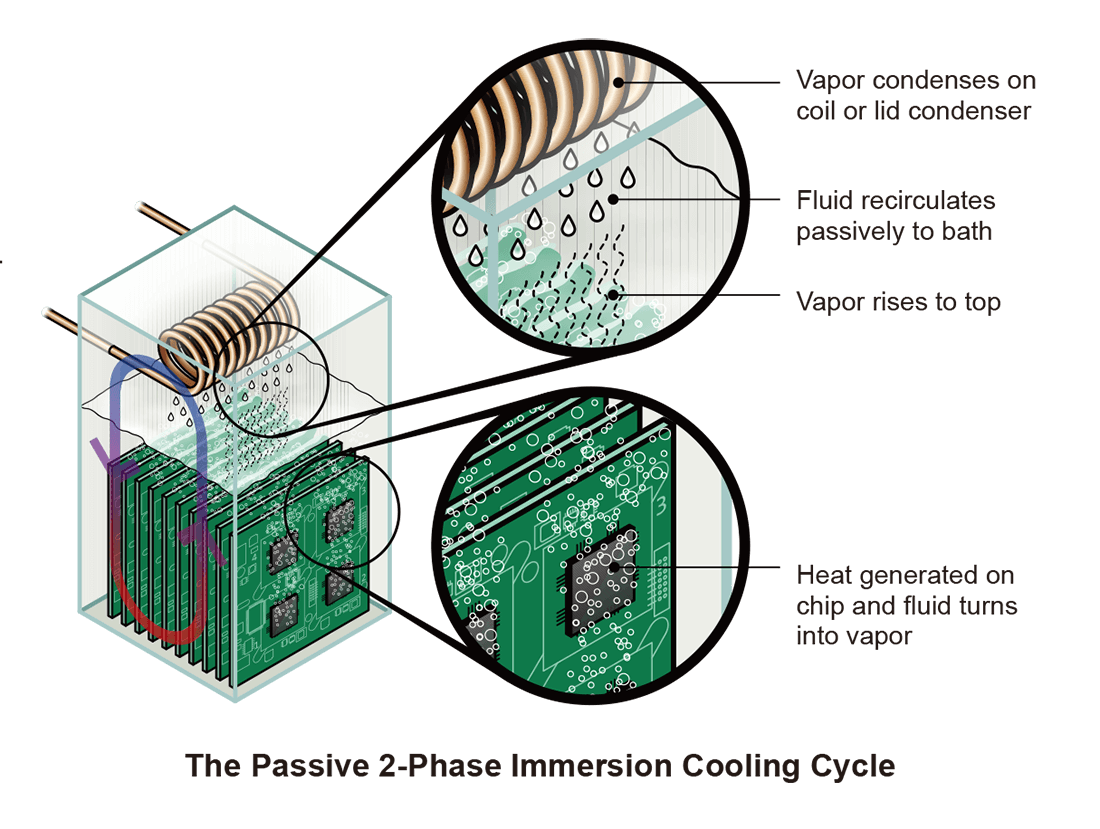
Although two-phase immersion cooling has several different variations, LiquidStack technology uses an "open bath" system, using a tank which contains a larger body of dielectric liquid where multiple servers are immersed into the bath, sharing the same liquid. The open bath system is fully sealed and can be opened from the top to service IT equipment.
Immersion Cooling Solution Partners
Immersion Cooling Infrastructure – LiquidStack
Headquartered in Hong Kong, LiquidStack is a pioneer in building the most efficient cooling solutions for high density electronics, and the first to successfully implement immersion cooling technology in commercial operations since 2012. LiquidStack have also created the world's largest immersion cooling data centers with 40MW and 120MW IT load capacities. They are an official technology partner of 3M and GIGABYTE for immersion cooling fluids, and have won the both the Data Center Dynamics "Future Thinking and Design Concepts” Award and the "Best Green ICT" Award for the most energy efficient Data center (PUE 1.01).
Headquartered in Hong Kong, LiquidStack is a pioneer in building the most efficient cooling solutions for high density electronics, and the first to successfully implement immersion cooling technology in commercial operations since 2012. LiquidStack have also created the world's largest immersion cooling data centers with 40MW and 120MW IT load capacities. They are an official technology partner of 3M and GIGABYTE for immersion cooling fluids, and have won the both the Data Center Dynamics "Future Thinking and Design Concepts” Award and the "Best Green ICT" Award for the most energy efficient Data center (PUE 1.01).
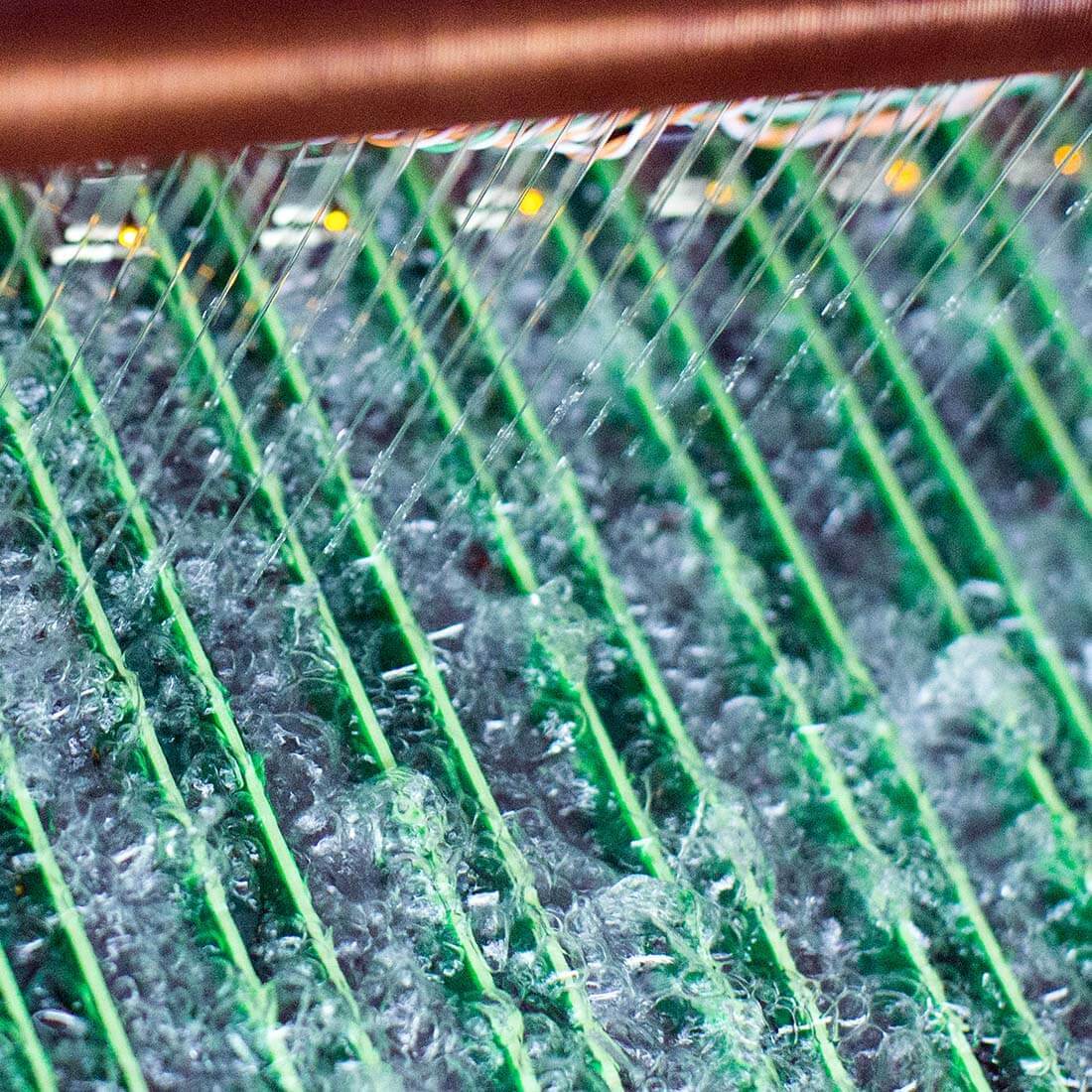

Immersion Cooling Fluid – 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids
3M has a long-held leadership position in immersion cooling fluids, beginning in the 1950s when 3M introduced its first dielectric fluorochemical heat transfer fluids for direct contact cooling for military avionics. Over the past five years, 3M engineered fluids have been used in server cooling and have been recognized by the industry for best in class energy efficiency.
GIGABYTE uses and recommends 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids fluids for a two-phase immersion cooling system. Fluorinert fluids are clear, colorless, non-conductive, non-flammable, residue free, thermally and chemically stable liquids. Fluorinert fluids have an extremely narrow boiling range, so the composition will not deviate with time, insuring consistent transport properties.
3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids have among the highest dielectric strength and electrical resistivity of all organic fluids, much better in fact than air. And unlike hydrocarbon liquids such as mineral oil, 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids are completely fluorinated. This means they have little or no solvency for hydrocarbons. Components taken out of 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids also dry out easily, and won't be wet, sticky or oily. There is no need to prepare rubber mats, tissues or other materials when taking the servers out of the liquid for maintenance.
3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids-Product Links
https://www.3m.com/3M/en_US/p/d/b10144228/
3M has a long-held leadership position in immersion cooling fluids, beginning in the 1950s when 3M introduced its first dielectric fluorochemical heat transfer fluids for direct contact cooling for military avionics. Over the past five years, 3M engineered fluids have been used in server cooling and have been recognized by the industry for best in class energy efficiency.
GIGABYTE uses and recommends 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids fluids for a two-phase immersion cooling system. Fluorinert fluids are clear, colorless, non-conductive, non-flammable, residue free, thermally and chemically stable liquids. Fluorinert fluids have an extremely narrow boiling range, so the composition will not deviate with time, insuring consistent transport properties.
3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids have among the highest dielectric strength and electrical resistivity of all organic fluids, much better in fact than air. And unlike hydrocarbon liquids such as mineral oil, 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids are completely fluorinated. This means they have little or no solvency for hydrocarbons. Components taken out of 3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids also dry out easily, and won't be wet, sticky or oily. There is no need to prepare rubber mats, tissues or other materials when taking the servers out of the liquid for maintenance.
3M™ Fluorinert™ Electronic Liquids-Product Links
https://www.3m.com/3M/en_US/p/d/b10144228/
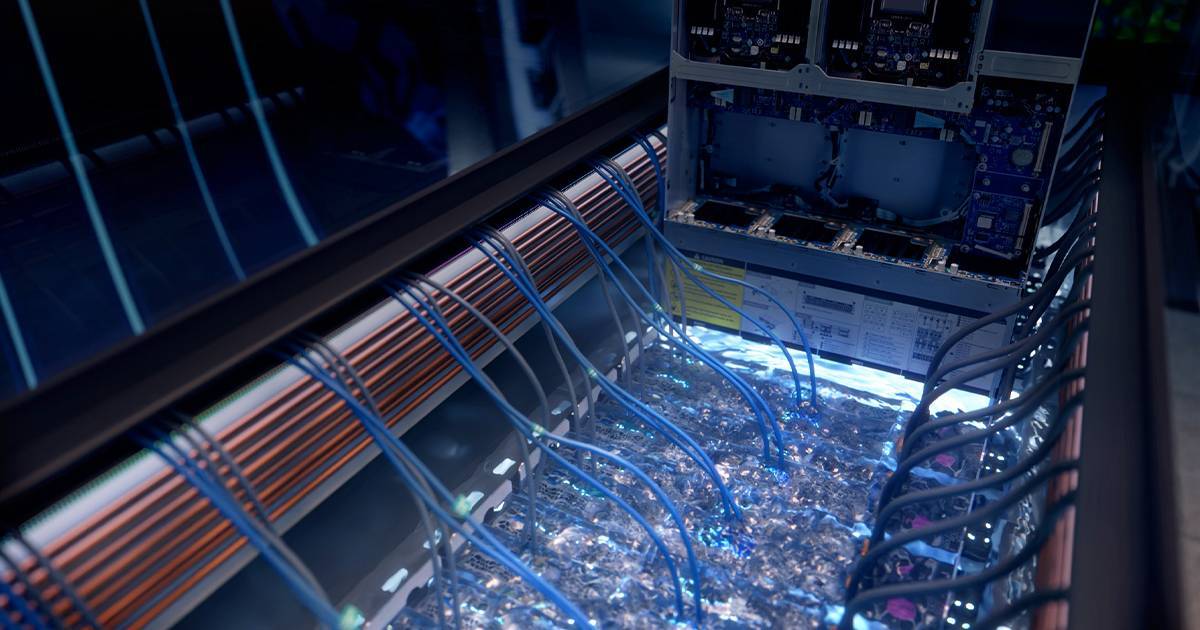
Immersion Cooling Servers with GIGABYTE
GIGABYTE is an industry leader in server systems for High Performance Computing, an application that is particularly suited to immersion cooling due to the high power consumption and heat generated by high performance processors. GIGABYTE can easily modify our standard server products to make them fully compatible with an immersion cooling system.









![[Success Case] Semiconductor Giant Selects GIGABYTE’s Two-Phase Immersion Cooling Solution](https://static.gigabyte.com/StaticFile/Image/Global/7d1140818ecc147f73f1fb239981e39b/Article/196)
![[Tech Guide] Two-phase and Single-phase Liquid Immersion Cooling](https://static.gigabyte.com/StaticFile/Image/Global/0480e97f1debff29e531921ca42a256c/Article/184)